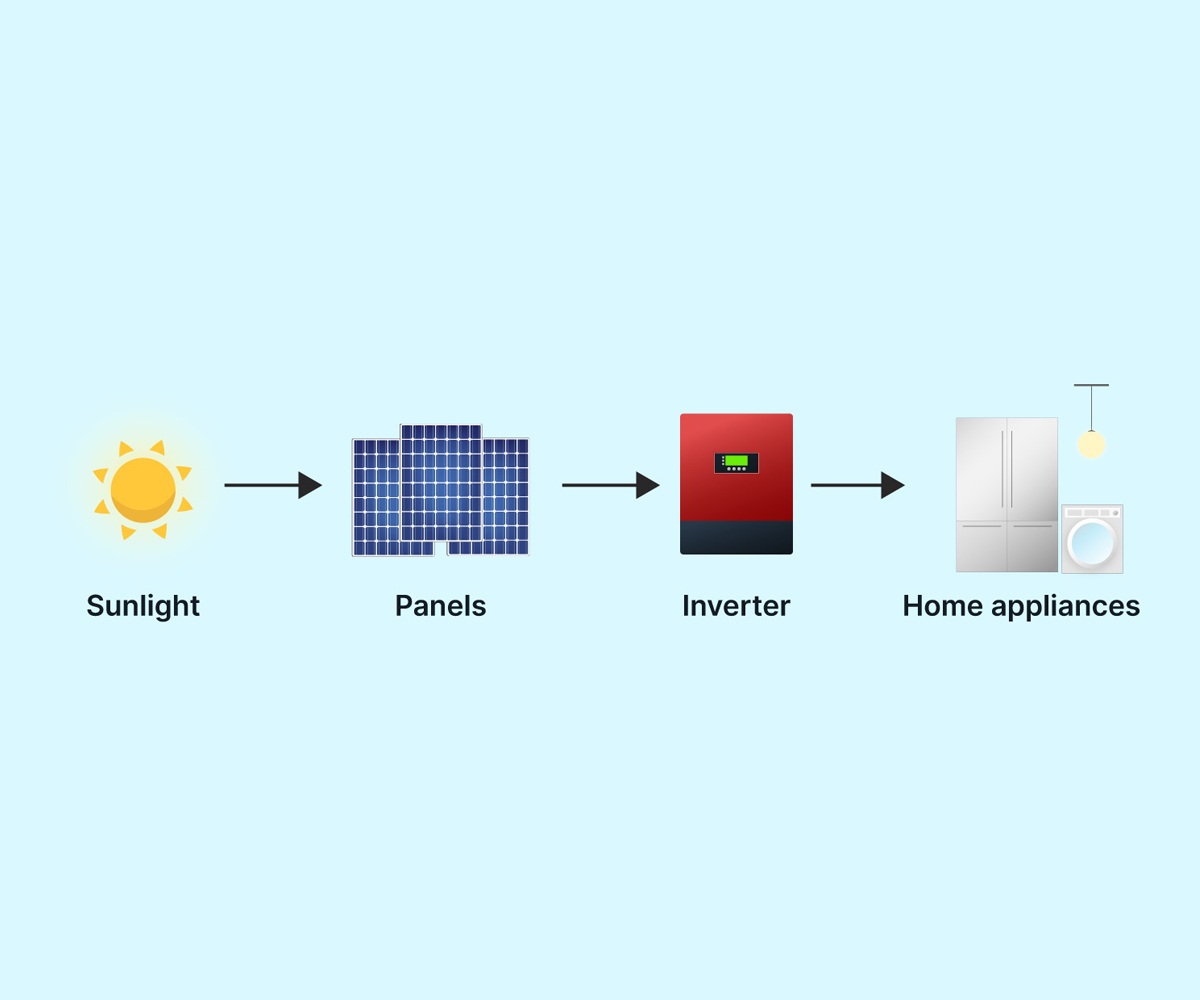
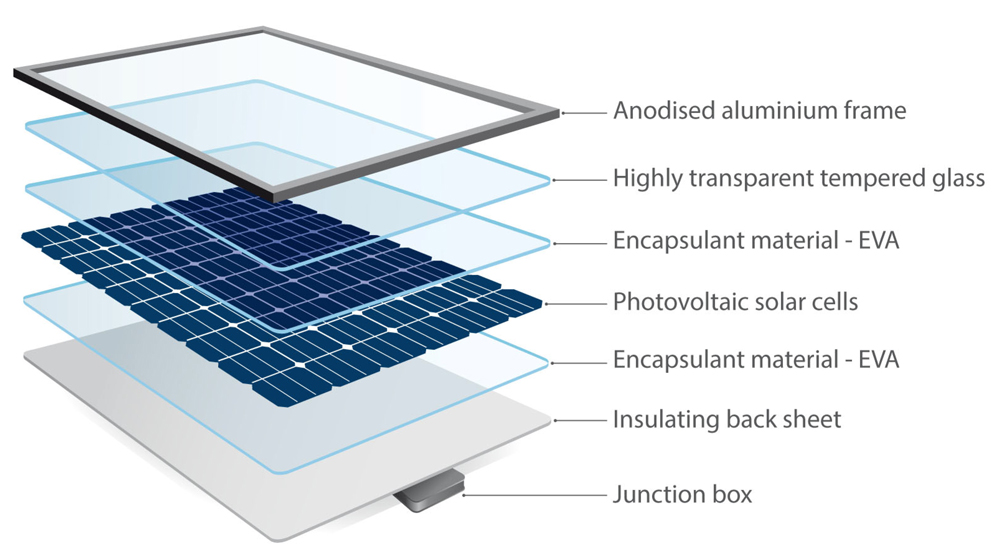
At the heart of every solar panel is a semiconductor material, usually made of silicon, which absorbs photons from the sun’s rays. When sunlight strikes the surface of the panel, the photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material, causing the electrons within the material to become energized and break free from their atomic bonds.
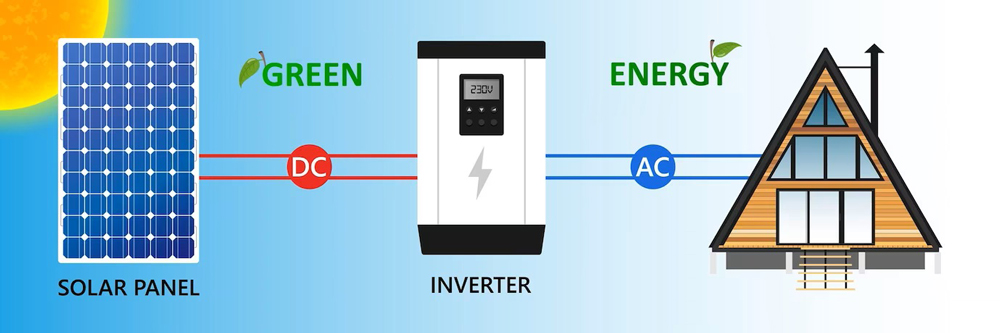
Once these free electrons are released, they can flow through the semiconductor material and create a flow of electricity. This flow of electrons is known as a direct current (DC), which can be used to power electronic devices or stored in batteries for later use.
But most of the electricity we use in our homes and businesses is in the form of alternating current (AC), which is why solar panels are connected to an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity that can be used to power household appliances and equipment.
The efficiency of a solar panel depends on several factors, including the quality of the semiconductor material, the amount of sunlight it receives, and the angle and orientation of the panel itself. Solar panels work best when they are installed in areas with high levels of direct sunlight, such as on rooftops or in open fields.
In recent years, advances in solar panel technology have made them even more efficient and affordable. New materials and designs have increased the amount of electricity that can be generated from a single panel, while improvements in manufacturing processes have brought down the cost of solar panels and made them more widely available.
In conclusion, solar panels generate electricity by converting sunlight into DC electricity, which is then converted into AC electricity by an inverter. While the efficiency of solar panels can vary depending on several factors, advances in technology have made them an increasingly popular and cost-effective source of renewable energy. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and move towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.