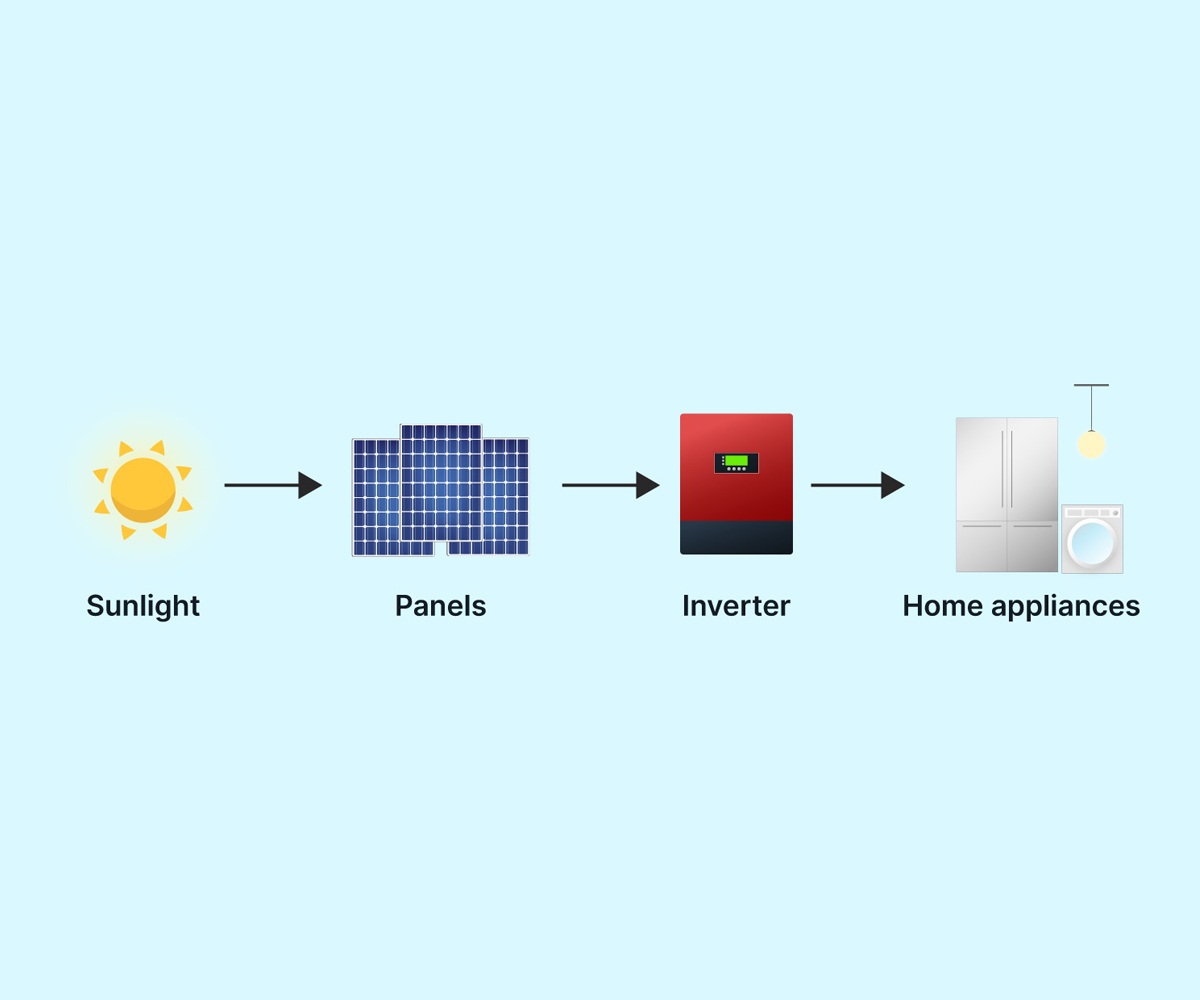
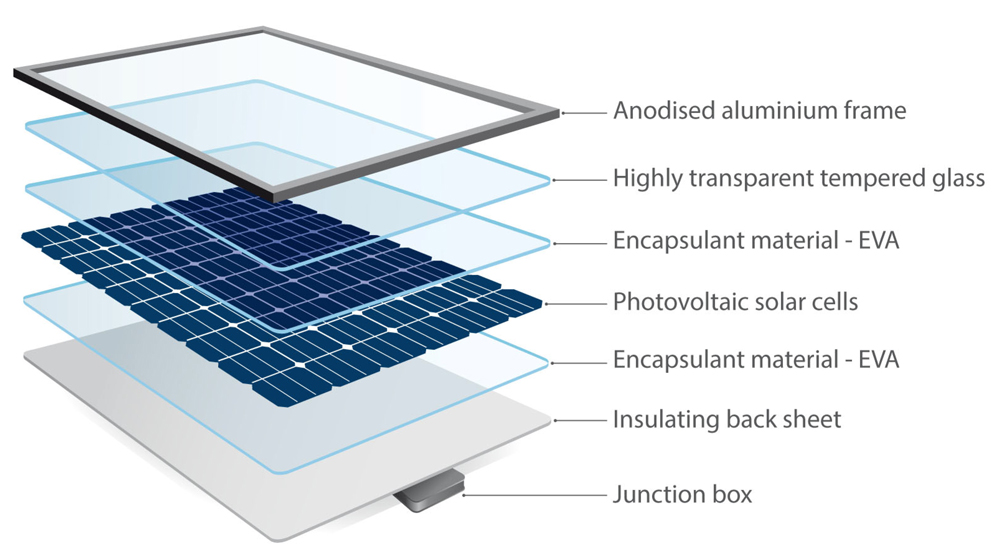
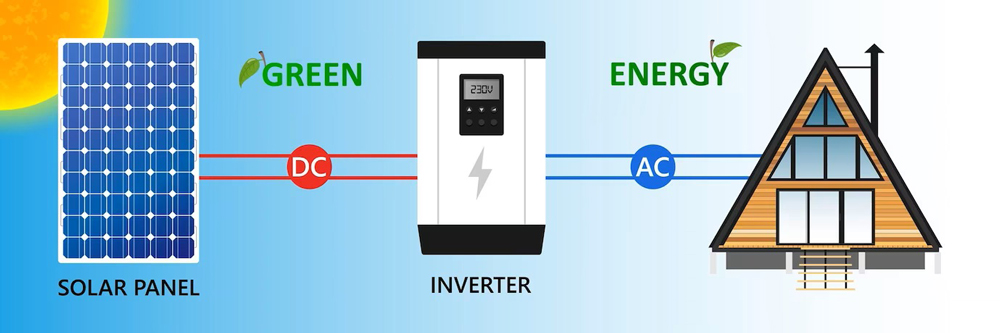
1) Energy Independence
Solar panels provide energy independence by reducing reliance on traditional power sources and the risk of power outages. Solar energy systems can be scaled up or down depending on a business’s energy needs for all size of businesses and able to store excess solar energy generated and can be used during periods of high demand or when solar generation is low.
2) Cost Savings
By generating their own electricity, businesses can reduce their dependence on the grid and avoid rising electricity costs. According to a report by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), businesses in India can save up to 50% on their electricity bills by switching to solar energy. Additionally, businesses that invest in solar energy can take advantage of government incentives such as accelerated depreciation and tax benefits, which can further reduce the cost of solar installations.
3) Government Incentives & Tax Benefits:
Governments around the world offer various incentives to encourage businesses to invest in solar energy. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and grants.
- Accelerated Depreciation: Businesses can claim up to 40% depreciation in the first year on solar panel systems under section 32 of the Income Tax Act, reducing their taxable income and lowering their tax liability.
- Interest Subsidy: The Indian government, through the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), provides interest subsidies for solar projects in India ranging from 2% to 5.25% of the total project cost, depending on the project type and size.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) exemption: Solar panels and related equipment are exempt from GST in India, providing a 5-18% reduction in costs depending on the state in which the solar panels are purchased.
- Capital Subsidy: The government provides a capital subsidy of 15% to 40% of the project cost for setting up solar power plants, depending on the size and type of project.
- Income Tax: Section 80-IA of the Income Tax Act provides a tax holiday for a period of 10 consecutive years to businesses that generate power from renewable energy sources, including solar energy.
4) Reduce carbon footprint
Switching to solar energy can significantly reduce a business’s carbon footprint. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), a typical 100 kW solar panel system can offset approximately 180 tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions annually. This is equivalent to planting 4,000 trees or taking 34 cars off the road each year. By reducing their emissions, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and contribute to a more eco-friendly future. Additionally, solar energy generates electricity without producing any harmful emissions, making it a clean and renewable source of energy.
5) Brand Reputation
By adopting solar energy, businesses can create a unique and positive brand image that is associated with sustainability and environmental responsibility. In today’s world, consumers are increasingly concerned about the impact of businesses on the environment and are more likely to support companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and trust, as well as positive media coverage.

6) ROI & Long-Term Investment
Investing in solar energy provides businesses with long-term cost savings and a positive ROI. International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports that solar power is cheaper than fossil fuels in most countries due to falling panel costs and increased efficiency. Lawrence Berkeley National Lab found that commercial properties with solar installations sell for 16% more on average, enhancing both ROI and property value.
7) Sell Carbon Credit and Net Metering
- Carbon Credit certificate: Businesses can sell their carbon credits certificate on carbon markets to other companies that need to offset their carbon emissions, generating additional revenue while helping to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Net Metering: Businesses can benefit from net metering, a system that allows them to sell excess energy generated by their solar panels back to the grid. This can help offset the initial cost of installing solar panels and generate additional revenue for the business.